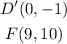Answer:
The coordinates of D' and F are;
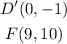
Step-by-step explanation:
Given the triangles DEF mapped onto D'E'F'.
Given then the coordinate;
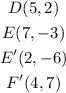
Let us find the translation used to map triangle DEF to D'E'F'.
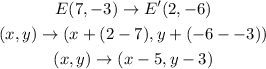
Applying the translation to point D;
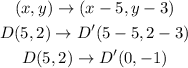
Also to get F;
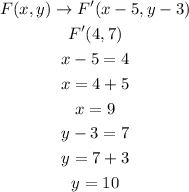
The coordinate of point F is;
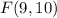
Therefore, the coordinates of D' and F are;