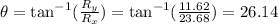Components:
First, calculate the cartesian components of each vector, as follow:
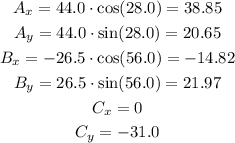
Next, consider that the components of the resultant vector R, are given by the sum of the x components and y components of all vectors A, B and C:
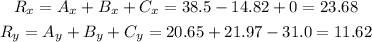
Magnitude:
The magnitude is calculated as follow:
![R=\sqrt[]{R^2_x+R^2_y}=\sqrt[]{(23.68)^2+(11.62)^2}=26.38](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/1zednphge5vi2oi4g12uf8ltm7tevst520.png)
Angle with x axis:
The angle related to the x axis is obtained as follow:
The tangent of the angle related to the x axis is:
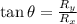
which is basically, the quotient between the opposite site and adjacent side of a right triangle formed by the components of the vector.
To obtain the angle you apply tan^-1 to cancel out the tangent, as follow: