We have a table for the probability distribution P(X) for the discrete variable x.
1) We must calculate the mean value μ of the variable x, using the following formula and the data from the table we have:
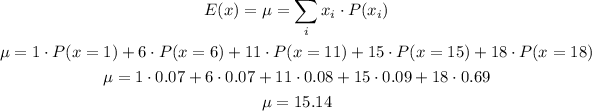
2) We must calculate the variance σ² of the variable x, using the following formula and the data from the table we have:
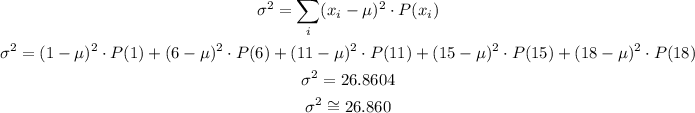
3) We calculate the standard deviation σ of the variable x simply taking the square root of the variance σ²:
![\begin{gathered} \sigma=\sqrt[]{\sigma^2} \\ \sigma=\sqrt[]{26.8604} \\ \sigma\cong3.891 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/7f2eoy1linyab9fv55bvkc4am25i4zkdkq.png)
4)