Let x be the unknown positive real number. Then, we can write our statement mathematically as
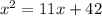
then, by moving the right hand side, we have
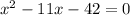
and we can solve this equation by means of the quadratic formula
![x=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{b^2-4ac}}{2a}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/rxvf73usjbbwyik14knxdemoz21vfz2ufc.png)
where, in our case, a=1 (the coefficient of x squared), b =-11 and c=-42. By substituting these values into the last formula, we get
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{-(-11)\pm\sqrt[]{(-11)^2-4(1)(-42)}}{2(1)} \\ x=\frac{11\pm\sqrt[]{121+168}}{2} \\ x=\frac{11\pm\sqrt[]{289}}{2} \\ x=(11\pm17)/(2) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/87b5sd6kwo9sdenlquvnonhtex3d2q39hv.png)
the first solution is given by taking the + sign and the secon solution with the - sign. Then, we have
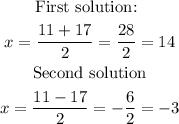
However, we need the positive real number. Then, the solution must be x=14.