Answer:
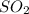
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the limiting reagent
The limiting reagent will be the reactant that produces less amount of the product
This is indicated by the number of moles of the product each of the reactant produce. The reactant that produces less product in terms of the number of moles is the limiting reactant.
The atomic mass of sulfur is 32 amu, while the molar mass of the oxygen molecule is 32 g/mol
To get the number of moles, we divide the mass by the molar mass/atomic mass
6.3g S translates to:
6.3/32 = 0.196875 mol
From the equation of reaction,
2 moles S gave 2 mol SO3
That means 0.196785 mol S will give 0.196785 mol SO3
Let us get for oxygen
10g of O2 will translate to:
10/32 = 0.3125 mol
From the equation of reaction:
3 mol O2 gave 2 mol SO3
0.3125 mol O2 will give: (0.3125*2)/3 = 0.2083 mol
As we can see, O2 gave the higher number of moles
This makes SO2 the limiting reactant