Use the Ideal Gas Law to find the pressure of the gas under the given conditions:
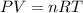
Where P represents pressure, V represents volume, n represents the amount of substance of the sample, R is the universal gas constant and T represents the temperature.
The volume and the temperature of the sample are given. On the other hand, we can calculate the amount of substance from the given mass of the sample. The molar mass M of a substance is the ratio between the mass of a sample and the amount of substance, and is characteristic of each substance:
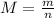
A molecule of O₂ is made of two oxygen atoms. The atomic mass of oxygen is approximately 16u, then, the atomic mass of the molecule of O₂ is 32u, which means that its molar mass is 32 grams per mole:
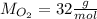
Isolate n from the equation and replace m=1g and M=32g/mol to find the amount of substance of the sample:
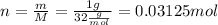
Now that we have calculated the value of n, the only unknown for the Ideal Gas Law is the pressure of the gas. Write the universal gas constant using units of liters for the volume:
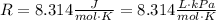
Isolate P from the ideal gas law and replace V=4.00L, n=0.03125mol, T=293K and the value of R to find the pressure of the gas:
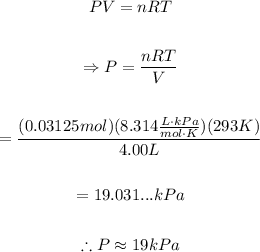
Therefore, the pressure of the container will be approximately 19kPa.