Solution:
Given the functions
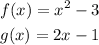
PART 1:
Concept:
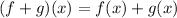
By applying the rule above, we will have
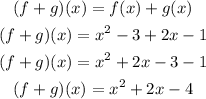
To figure out (f+g)(2) means that we are going to substitute the value of x as 2
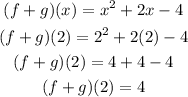
Hence,
(f+g)(2) = 4
PART 2:
Concept:
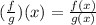
By applying the rule above, we will have
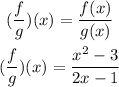
To figure out the value of (f/g)(-1) means we will substitute the value of x=-1
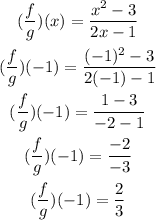
Hence,
(f/g)(-1) = 2/3
PART 3:
To figure out the domain of (f.g)(x)
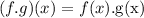
By applying the formula above, we will have
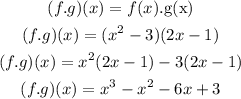
Hence,
The domain of the above set of equations is given below as
[tex]=\quad \begin{bmatrix}\mathrm{Solution\colon}\: & \: -\infty\: