Answer:
3.54 L of hydrogen gas (H2).
Step-by-step explanation:
What is given?
Volume (V) = 3.55 L.
Pressure (P) = 755 torr = 0.993 atm. (1 atm = 760 torr)
Temperature (T) = 29.0 °C + 273 = 302 K.
R = 0.082 atm*L/mol*K.
Step-by-step solution:
Let's use the ideal gas formula:
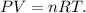
Where P is pressure, V is volume, n is the number of moles, R is the ideal gas constant and T is the temperature on Kelvin scale. Let's solve for 'n', the number of moles of chlorine gas (Cl2):
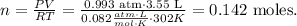
Now, let's see how many moles of H2 are required to react with 0.142 moles of Cl2.
In the chemical equation, you can see that 1 mol of H2 reacts with 1 mol of Cl2 too, so the molar ratio between them is 1:1. This means that 0.142 moles of Cl2 will react with 0.142 moles of H2 too.
As they're reacting in a determined place with given pressure and temperature conditions, we just have to replace 'n = 0.142 moles H2' when we solve for 'V', like this:
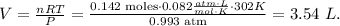
The answer is that we require 3.54 L of hydrogen gas (H2) to react with chlorine gas (Cl2).