We are given the following data
Significance level = 0.1
For the first data
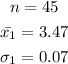
For the second data
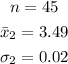
We can get the test statistic as follow
![z=\frac{\bar{x_1-}\bar{x_2}}{\sqrt[]{(\sigma^2_1)/(n_1)+(\sigma^2_2)/(n_2)}}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/y850vvuxn8var89qddcvd405t3chqfmn48.png)
Thus
![\begin{gathered} z=\frac{3.47-3.49}{\sqrt[]{(0.07^2)/(45)+(0.02^2)/(45)}}=(-0.02)/(0.01085)=-1.842 \\ z=-1.84 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/7vz2r60wkwlz53gfp5dj2tj7f0t67xgdhi.png)
The test statistic is the z-score above = -1.84
The p-value of the z-score value obtained above is found out to be 0.07
Since the p-value obtained is less than the significance level, we will reject the null hypothesis