Answer:
The alpha decay of Th-232 produces the nucleotide radium-228 (Ra-228):
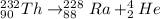
Step-by-step explanation:
The question requires us to write the chemical reaction that represents the alpha decay of Thorium-232 (Th-232).
Nuclear chemistry > Types of radioactive decay
Alpha decay corresponds to the emission of an alpha (α) particle - two protons and two neutrons - from the nucleus. A generic representation of an alpha decay reaction is as follows:
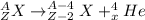
Therefore, an alpha decay produces a daughter nucleotide with atomic number = Z-2 and atomic mass = A-4.
For Thorium-232, the alpha decay reaction can be written as follows (keep in mind that thorium presents atomic number = 90 and the atomic mass of the considered isotope, Th-232, is 232 a.u.):
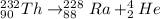
The alpha decay of Th-232 produces the nucleotide radium-228 (Ra-228).