Part (1)
The free body daigram of the block on the inclined plane can be shown as,
According to work energy theorem,
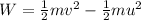
The work done on the block can be expressed as,
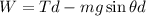
Plug in the known expression,
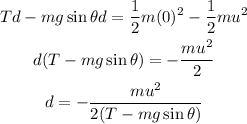
Substitute the known values,

Thus, the distance travelled by the block is 4.60 m.
Part (2)
The work done by gravitational force is given as,
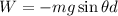
Substitute the known values,
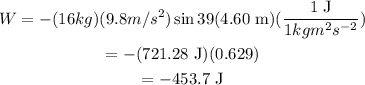
Thus, the work done by gravitational force is -453.7 J.