Given data:
* The mass of the Moon is 0.0123 times of mass of Earth as,
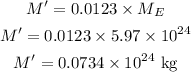
where M_E is the mass of Earth,
* The radius of the Moon is 0.272 times the mass of Earth as,
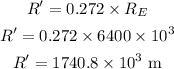
where R_E is the radius of Earth,
Solution:
The escape velocity of the object from the surface of the Moon is,
![v_e=\sqrt[]{(2GM^(\prime))/(R^(\prime))}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/cdwez3bkjxsylivopaum6kf8tsbsza8svz.png)
where G is the gravitational constant, M' is the mass of Moon, and R' is the radius of Moon,
Substituting the known values,
![\begin{gathered} v_e=\sqrt[]{(2*6.67*10^(-11)*0.0734*10^(24))/(1740.8*10^3)} \\ v_e=0.0237*10^5ms^(-1) \\ v_e=2.37*10^3ms^(-1) \\ v_e=2.37kms^(-1) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/kebmc0ysebobcdj16iu2khk87wawxnzn69.png)
Thus, the escape velocity on the Moon is 2.37 Kilometers per second.