Firstly we will convert the mass of the reactants to moles or reactants:
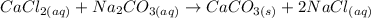
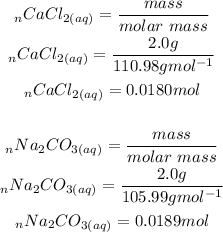
The easiest way to determine which is the limiting reagent is to determine the moles per co-efficient ratio.
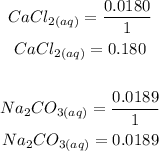
Answer: The one with the lowest value is the limiting reactant. CaCl2 has the lowest value and is the limiting reactant.