The equation for the Kp is the multiplication of the products exponentiated by its stoichiometric coefficients divided by the same for the reactants.
In this case, we have a single product, NO₂ (g), with stoichiometry 2, and a single reactant, N₂O₄ (g), with stoichiometry 1. So, the equation for Kp, is:
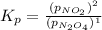
Since we know that the equilibrium was reached where:
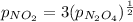
So, we can substitute that into the Kp equation to get:
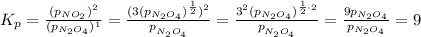
So, the Kp for this temperature must be 9.