Answer:
The partial pressure of carbon dioxide is 22.1mmHg.
Step-by-step explanation:
The total pressure is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of all the gases in the container:
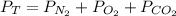
So, replacing the total pressure (83.4mmHg), the partial pressure of oxygen (15.5mmHg) and the partial pressure of nitrogen (45.8mmHg), we can calculate the partial pressure of the carbon dioxide:
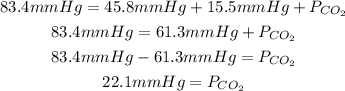
Finally, the partial pressure of carbon dioxide is 22.1mmHg.