Step 1
The reaction involved:
CO + 2 H2 → CH3OH (completed and balanced)
------------
Step 2
Data provided:
19.7 g H2 (the limiting reactant)
Excess reactant = CO
144.5 g CH3OH = actual yield
----
Data needed:
The molar masses of:
H2) 2.00 g/mol
CH3OH) 32.0 g/mol
-----------
Step 3
The theoretical yield:
By stoichiometry,
CO + 2 H2 → CH3OH (The molar rate between H2 and CH3OH = 2:1)
2 x 2.00 g H2 --------- 32.0 g CH3OH
19.7 g H2 --------- X
X = 19.7 g H2 x 32.0 g CH3OH/2 x 2.00 g H2
X = 157.6 g CH3OH (The theoretical yield)
-----------
Step 4
The % yield is defined as follows:
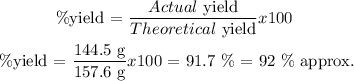
Answer: d. 93% (it is the nearest value in comparison to my result)