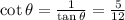Answer:
• The length of the missing side is 13.
,
• sin θ = 12/13, cos θ=5/13, tan θ = 12/5
,
• cosec θ = 13/12, sec θ = 13/5, cot θ = 5/12
Explanation:
Part A
First, we find the length of the missing side, MT using the Pythagorean Theorem.
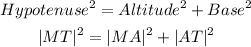
Substitute the known values:
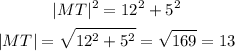
The length of the missing side is 13.
Part B
Next, we find the six trigonometric ratios of θ.
• The side ,opposite angle ,θ = 12
,
• The side ,adjacent to ,angle θ = 5
,
• The ,hypotenuse ,= 13
(i)sin θ
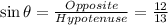
(ii)cos θ
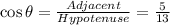
(iii)tan θ
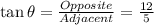
(iv)cosec θ
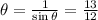
(v)sec θ
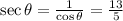
(vi)cot θ