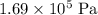Given data:
* The given section with the diameter d_1 = 5.5 cm.
* The flow speed of the fluid in the section with the diameter d_1 is v_1 = 715 cm/s.
* The diameter of the other section is d_2 = 4.6 cm
* The density of the fluid is,
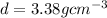
* The pressure of fluid in the section with diameter d_1 is,
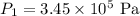
Solution:
(A). The flow rate of the fluid remains constant, thus,
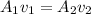
where A_1 is the area of the section with diameter d_1, A_2 is the area of the other section with diameter d_2, and v_2 is the velocity of the fluid in section with diameter d_2,
The area of the section with diameter d_1 is,
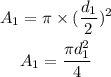
Substituting the known values,
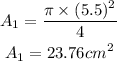
The area of the other section of pipe with diameter d_2 is,
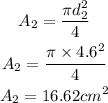
Thus, the velocity of the fluid from the other section with diameter d_2 is,
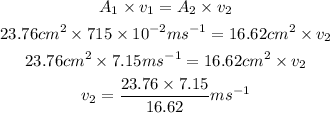
By simplifying,
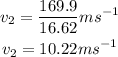
Thus, the velocity of the fluid from the other section with a diameter of 4.6 cm is 10.22 m/s.
(B). From Bernoulli's principle, the relation between the pressure and velocity on each section is,
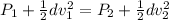
where d is the density of the fluid, P_1 is the pressure of fluid in the section with diameter d_1 and p_2 is the pressure of the fluid in the section with the diameter d_2,
Substituting the known values,
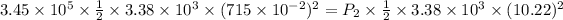
By simplifying,
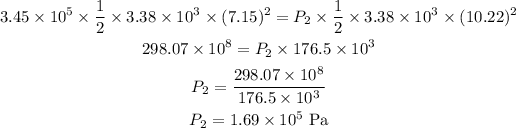
Thus, the pressure of fluid in the section with a diameter of 4.6 cm is,