Using the trigonometric functions in a right triangle,
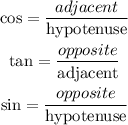
The right triangle can be resketched to get the third unknown angle;
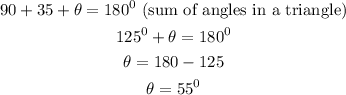
Considering angle 55 degrees as a reference,
side y is the adjacent and side 20 is the hypotenuse.
Thus, the trigonometric identity that combines adjacent and hypotenuse is cosine.
Therefore,
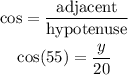
Thus, the first option is correct.