Answer tab
The force on a moving particle can be written as:
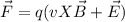
Where X is the vectorial product. In our case, as there is only a magnetic field, we'll have:
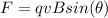
Where theta is the angle between both vectors. Replacing our values we get:
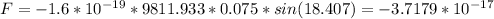
Considering we want only the magnitude (not the signal) and in terms of 10^(-19), our final answer is:
F = 371.79 * 10^(-19) N