Solve the given simultaneous equation to find the value of y:
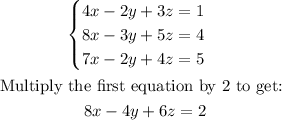
Subtract the new equation from the second equation:
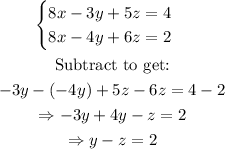
Multiply the first equation by 7 and the last equation by 4, then subtract:
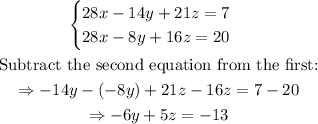
Combine this equation with the first one derived, y-z=2.
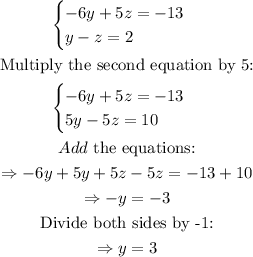
Hence, the value of y is 3.
The correct option is A.