We have the function:
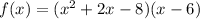
We already have one of the roots (x=6).
We can factorize the quadratic factor in order to find the other roots:
![\begin{gathered} x=\frac{-2\pm\sqrt[]{2^2-4\cdot1\cdot(-8)}}{2} \\ x=-1\pm\frac{\sqrt[]{4+32}}{2} \\ x=-1\pm\frac{\sqrt[]{36}}{2} \\ x=-1\pm(6)/(2) \\ x=-1\pm3 \\ x_1=-1-3=-4 \\ x_2=-1+3=2 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/rwnqn3gsabqho2ai6d57ootm1xq4qz7ki8.png)
We then can write f(x) as:
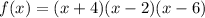
being the zeros x=6, x=-4 and x=2.
In coordinates, this zeros are represented by the points (6,0), (-4,0) and (2,0).
Answer:
A. (2,0)
В. (6, 0)
D. (-4,0)