Let's sketch the problem to understand better:
Since the angle of reflection is congruent to the angle of incidence, we have r1 = i1 = 38.2°.
Now, let's calculate angle x, knowing that it is complementary to the angle r1:
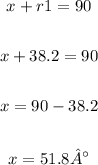
To calculate angle y, let's add all angles in the triangle and equate the sum to 180°:
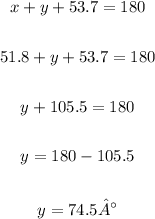
Angles i2 and y are complementary, so we have:
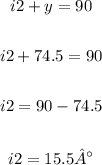
Since r2 and i2 are congruent, so the angle of reflection in the second mirror is 15.5°.