Step-by-step explanation
We consider a vector with:
• initial point (x₁, y₁) = (4, 3),
,
• final point (x₂, y₂) = (-4, -1).
The magnitude of the vector is given by:
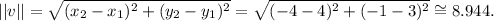
The angle of the vector is given by:
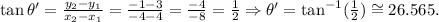
We have obtained a positive value of the angle θ'. But we see that our vector points in the negative direction. To take into account this, we must sum 180° to this result:
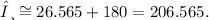
Answer
||v|| = 8.944, θ = 206.565°