Answer
-1430 kJ
Step-by-step explanation
Given information:
From 1; ΔH for the formation of 1 mol CO₂(g) = -394 kJ. For 2 mol CO₂(g), ΔH will be (2 x -394 kJ) = -788 kJ
From 2; ΔH for 1 mol H₂O(l) = -242 kJ. For 3 mol H₂O(l), ΔH will be (3 x -242 kJ) = -726 kJ
From 3, ΔH for 1 mol C₂H₆ = -84 kJ.
ΔHc for the given reaction can be calculated using the formula below:

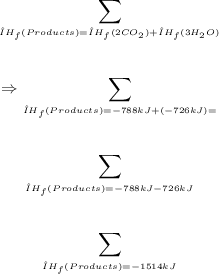
For the reactants,
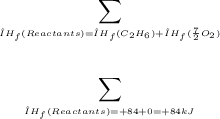
Therefore, ΔHc for the given reaction is:
ΔHc = -1514 kJ - (-84 kJ)
ΔHc = -1514kJ + 84 kJ
ΔHc = -1430 kJ