The general gas law states that the product of the pressure and the volume of the gas, divided by the thermodynamic temperature, in kelvin, is equal to a constant. This constant, in turn, is described by the Clapeyron equation, note:
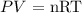
Where:
P = pressure exerted by the gas
V = volume occupied by this gas
T = temperature in kelvin
R = universal ideal gas constant (0.082 atm.L/mol.K)
n = number of moles
Step 1 - Transform 20 °C into kelvin using the formula: Tk = 273 + Tc
Tk = 273 + 20
Tk = 293 K
Step 2 - Replace the values on the formula:
P = 0.900 atm
V = 8.50L
n = ???
R = 0.082 atm.L/mol.K
T = 293
PV = nRT
0.900 x 8.50 = n x 0.082 x 293
n = 0.106/24.026
n = 0.004407 moles of oxygen
Step 3 - We transform moles into gram using the formula: mass = moles x molar mass
molar mass of O2 = (2x16) = 32 g/mol
mass = 0.004407 x 32
mass = 0.141 grams of O2
Answer: 0.141 grams of O2