We are given that an object is moving north at a speed of 5 m/s, lets call this object 1. We have another object moving west at a speed of 2 m/s, this is object 2. A diagram of the problem is the following:
To determine the loss in kinetic energy we need to determine the difference in kinetic energy before the collision and after the collision:
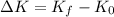
The final kinetic energy is:
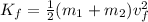
We use the sum of the masses because the objects are stuck together after the collision. The initial kinetic energy is:
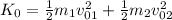
Substituting we get:
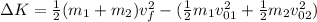
The only missing variable is the final velocity. To determine the final velocity we will use the conservation of momentum.
We will use the conservation of momentum in the horizontal direction (west) and the conservation of momentum in the vertical direction (north).
In the horizontal direction we have:
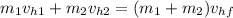
Since the object 1 has no velocity in the horizontal direction we have that:
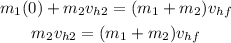
Now we solve for the final horizontal velocity:
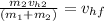
Now we substitute the values:
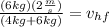
Solving the operations we get:
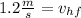
Now we use the conservation of momentum in the vertical direction, we get:
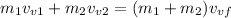
Since the second object has no vertical velocity we get:
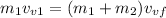
Now w solve for the final vertical velocity, we get:
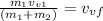
Now we substitute the values:
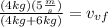
Now we solve the operations:
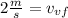
Now we determine the magnitude of the final velocity using the following formula:
![v_f=\sqrt[]{v^2_(hf)+v^2_(vf)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/kl80w2rzo1bdgferd4fvtgh99ats0edt4l.png)
Substituting the values:
![v_f=\sqrt[]{(1.2(m)/(s))^2+(2(m)/(s))^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/physics/college/3ga6qjutwmw0n2m3su5uco9ajvwwvpzzh3.png)
Solving the operations:
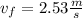
Now we substitute this in the formula for the kinetic energy and we get:
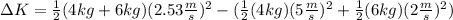
Solving the operations:
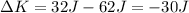
Therefore, there was a loss of 30J of kinetic energy.