![undefined]()
1) We have here a right triangle, so we can use the Pythagorean Theorem to find the adjacent leg. Note that the hypotenuse is leg opposite to the right angle. In this case, a=4.
a²=b²+c²
4²=b²+3²
16=b²+9
16-9=b²
b=√7
2) Let's find the trigonometric functions. The first one is the sine (θ), which relates the opposite side and the hypotenuse:
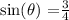
2.2)Moving on, we can deal with the tangent of theta, relating the opposite side over the adjacent, for this one we have to rationalize it:
![\begin{gathered} \tan (\theta)\text{ =}\frac{3}{\sqrt[]{7}} \\ \tan (\theta)=\frac{3\sqrt[]{7}}{7} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/xaokyvz9fdzouel7iyfw94ywir5r27t5ki.png)
Finally, let's find the reciprocal function of the cosine function by setting this as the reciprocal of the cosine, and then calculating it:
![\begin{gathered} \sec \text{ (}\theta)=(1)/(\cos(\theta))\Rightarrow\sec (\theta)=\frac{1}{\frac{\sqrt[]{7}}{4}}\Rightarrow\sec (\theta)\text{ =}\frac{4}{\sqrt[]{7}} \\ \sec (\theta)\text{ =}\frac{4\sqrt[]{7}}{7} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/ts6n1g1aqff0vbegvcicv6g4kdetnky3j2.png)