The standard heat of formation of Compound X at 25 °C is approximately
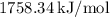 (rounded to three significant digits).
(rounded to three significant digits).
To calculate the standard heat of formation
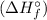 for Compound X, we can use the equation:
for Compound X, we can use the equation:
![\[ q = mc\Delta T \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/xkse0tnkvd4vvl2mwyzbhxv5iwqi1fuzdk.png)
where:
-
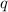 is the heat absorbed by the water,
is the heat absorbed by the water,
-
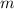 is the mass of water,
is the mass of water,
-
 is the specific heat of water, and
is the specific heat of water, and
-
 is the change in temperature.
is the change in temperature.
The heat absorbed by the water is equal to the heat released by the combustion of Compound X:
![\[ q = \Delta H_f^\circ * n \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/7yyt00say3fpke88tqr3v7jbwjgqcki4d0.png)
where:
-
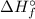 is the standard heat of formation per mole of Compound X, and
is the standard heat of formation per mole of Compound X, and
-
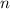 is the number of moles of Compound X.
is the number of moles of Compound X.
First, calculate the number of moles of Compound X:
![\[ \text{Molar mass of }C_3H_4 = (3 * \text{atomic mass of C}) + (4 * \text{atomic mass of H}) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/vu5mj5eoh63219mr8wppuhhqpyml6z0apz.png)
Now, determine the number of moles
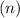 :
:
![\[ n = \frac{\text{mass of Compound X}}{\text{molar mass of Compound X}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/yf1w1mov5rc3r3briumlh0ys5hw1j4vdzn.png)
Next, calculate the heat
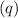 absorbed by the water using the first equation:
absorbed by the water using the first equation:
![\[ q = mc\Delta T \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/xkse0tnkvd4vvl2mwyzbhxv5iwqi1fuzdk.png)
Finally, use the second equation to find
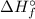 :
:
![\[ \Delta H_f^\circ = (q)/(n) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/4hwudltbwhqkqt0sg14z4rg2rjiz8ast5o.png)
Now, let's perform the calculations:
![\[ \text{Molar mass of } C_3H_4 = (3 * 12.01 \, \text{g/mol}) + (4 * 1.01 \, \text{g/mol}) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/9ike8mkmuyhgutgtu9alm1hhv09500yea9.png)
![\[ = 36.03 + 4.04 = 40.07 \, \text{g/mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/1yntcim7k5i5dwub2hbvyjnu76i71b7d8i.png)
![\[ n = \frac{6.000 \, \text{g}}{40.07 \, \text{g/mol}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/9m5xvsho7nu2zvannm1d3awy9gqvwb4snt.png)
![\[ \approx 0.1497 \, \text{mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/8xrxxxtrktynowb61xpvf69dh9coi55xgv.png)
![\[ q = (25.00 \, \text{kg}) * (4.18 \, \text{J/g}^\circ\text{C}) * (2.656 \text{\textdegree C}) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/qespj83k8knin9pege20cnke67y9ff3apo.png)
![\[ = 263.124 \, \text{kJ} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/5vg4yc4m00hjaaig5yic03uolh1pp3ptaa.png)
![\[ \Delta H_f^\circ = \frac{263.124 \, \text{kJ}}{0.1497 \, \text{mol}} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/szo3t3ah9ngai6dusxrqq6anu1kc0kruwr.png)
![\[ \approx 1758.34 \, \text{kJ/mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/chemistry/college/oab79zxzbf0bnk90bnyso4hh0g709g5rff.png)
So, the standard heat of formation of Compound X at 25 °C is approximately
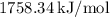 (rounded to three significant digits).
(rounded to three significant digits).