We have some registered values of mass and temperature, there is heating since the final temperature is higher than the initial one. Calculating the temperature difference consists of subtracting the final temperature minus the initial temperature. So we will have the following equation.
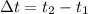
Now, for each reaction we have the following temperature change:
Reaction 1 (MgO)
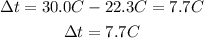
Reaction 2 (Mg)
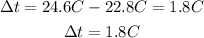
The change in temperature for reaction 1 is 7.7°C and for reaction 2 is 1.8°C