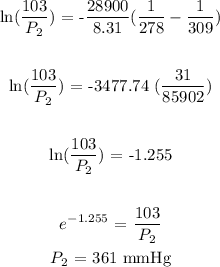Answer:
Step-by-step explanation:
Here, we want to get the vapour pressure of the compound at the given temperature
We can use the Clausius-Clapeyron equation for this
Mathematically, we have this as:
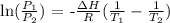
So,let us identify the values:
P1 = 103 mmHg
P2 = ?
ΔH = 28,900
R = 8.31
T1 = 278 K
T2 = 309 K
We now proceed to substitute these values into the equation above as follows: