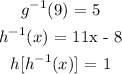Step 1: Write out the functions
g(x) = { (0.5), (2, 4), (4,6), (5,9), (9,0) }
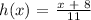
Step 2:
For the function g(x),
The inputs variables are: 0 , 2, 4, 5, 9
The outputs variables are: 5, 4, 6, 9, 0
The inverse of an output is its input value.
Therefore,
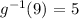
Step 3: find the inverse of h(x)
To find the inverse of h(x), let y = h(x)
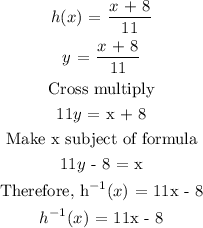
Step 4:
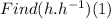
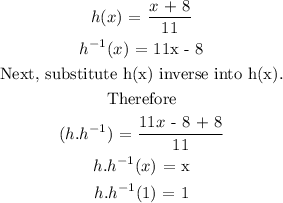
Step 5: Final answer