The claim is that the population mean for the smartphone carrier's data speed at airports is less than 4.00 Mbps
The parameter of the study is the population mean, symbolized by the Greek letter mu "μ"
The researchers believe is that his value is less than 4, you can symbolize this as:
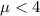
This expression does not include the "=" symbol, which indicates that it represents the alternative hypothesis. The null and alternative hypotheses are complementary, so if the alternative hypothesis represents the values of μ less than 4, then the null hypothesis, as its complement, should represent all other possible values, which are those greater than and equal to 4. You can represent this as:
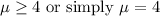
The statistical hypotheses for this test are:
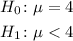
Option A.
In the display of technology, you can see the data calculated for the test.
The second value shown in the display corresponds to the value of the test statistic under the null hypothesis, you have to round it to two decimal places:
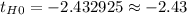
The value of the test statistic is -2.43
The p-value corresponds to the third value shown in the display.
The p-value is 0.009337
To make a decision over the hypothesis test using the p-value you have to follow the decision rule:
- If p-value ≥ α, do not reject the null hypotheses.
- If p-value < α, reject the null hypotheses.
The significance level is α= 0.05
Since the p-value (0.009337) is less than the significance level of 0.05, the decision is to reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion
So, at a 5% significance level, you can conclude that there is significant evidence to reject the null hypothesis (H₀: μ=4), which means that the population mean of the smartphone carrier's data speed at the airport is less than 4.00 Mbps.