Answer:
Explanations:
For a chemical reaction to be balanced, the total number of moles of elements at the reactant must be equal to the number of moles at the product.
Given the chemical reaction;
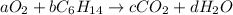
Equating the number of moles of elements on both sides:
For the oxygen element:
2a = 2c + d ................... 1
For the carbon element;
6b=c
For the Hydrogen element:
14b = 2d
7b = d .............................. 3
Assume a = 2;
Equation 1 becomes:
2(2) = 2c + d
4 = 2c + d ................,....4
From equation 2
b = c/6 .............................. 5
From equation 3:
b = d/7 ...................... 6
Equating 5 and 6
c/6 = d/7
7c = 6d
c = 6d/7 ........................... 7
Substitute equation 7 into 4 to have:
4 = 2c + d
4 = 2(6d/7) + d
4 = 12d/7 + d
4 = (12d+7d)/7
28 = 19d
d = 28/19
To get the value of b:
b = d/7
b = 28/19 * 1/7
b = 28/133