When we have a mixture of gases, the pressure exerted by each depends on the number of moles present in the mixture, this contribution is called partial pressure. The sum of the partial pressures will be equal to the total pressure, this is called Dalton's law.
Partial pressure can be described by the following equation:
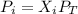
Where,
Pi is the partial pressure
Xi is the molar fraction
Pt is the total pressure
The molar fraction is calculated by the following equation:
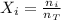
Where,
ni is the number of moles of the substance
nT is the total number of moles.
So, we have to find first the number of moles of each gas. We are given the grams of gases, to get the equivalent moles we must divide the mass by the molar mass.
Molar Mass N2=28.0134g/mol
Molar Mass O2=31.9988g/mol
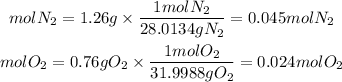
Now, the partial pressure of N2 will be:
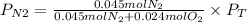
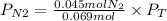
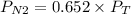
If we assume that the gas behavior is like an ideal gas, we can find the total pressure with the following equation:
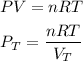
Where,
n is the total number of moles, 0.069mol
R is a constant, 0.08206atm.L/mol.K
V is the volume of the gas, 1.51L
T is the temperature of the gas, K.284.15K
We replace the known data:
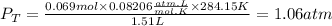
Now, the partial pressure of nitrogen will be:
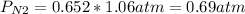
Answer: The partial pressure of N2 is 0.69atm