Answer: The oxidation states can be labelled as:
- In Fe2O3: Fe = +3, O = -2
- In CO: C = +2, O = -2
- In Fe: Fe = 0
- In CO2: C = +4, O = -2
Fe is being reduced (changes from +3 to 0) and C is being oxidized (changes from +2 to +4).
Step-by-step explanation:
The question requires us to label the oxidation states of each element in the following chemical equation, and then determine which one is being oxidized and which one is being reduced.
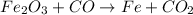
To solve this problem, we need to keep in mind a few points:
- oxidation occurs when its oxidation number increases (the element "loses" an electron);
- reduction occurs when its oxidation number decreases (the element "gains" an additional electron);
- the oxidation number of some elements is usually the same; a good example is oxygen (O): in most cases, O presentes oxidation number equals to -2.
Next, let's analyze the oxidation numbers of the elements in the reaction:
- Fe2O3: since O has oxidation number = -2, in the compound Fe2O3 the total charge brought by O is (-2) * 3 = -6, thus 3 atoms of Fe must have charge +6. We can say Fe has oxidation number = +3 in Fe2O3 (because (+3) * 2 + (-2) * 3 = 0).
- CO: O has oxidation number = - 2, thus C must present oxidation number = +2 in CO.
- Fe: Elementar Fe presents oxidation number = 0;
- CO2: Since O has oxidation number = -2, C must present oxidation number = +4 (because (+4) * 1 + (*2( * 2 = 0.
Thus, the oxidation states can be labelled as:
- In Fe2O3: Fe = +3, O = -2
- In CO: C = +2, O = -2
- In Fe: Fe = 0
- In CO2: C = +4, O = -2
Analyzing the oxidation states in the reactants (left side) and products (right side), we can see that Fe goes from +3 to 0, thus it is being reduced, while C goes from +2 to +4, thus it is being oxidized.