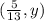
This is given point in the fourth quadrant.
In this point, the adjacent is
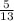
The opposite is y.
Find hypotenuse h using the pythagorean theorem:
![\begin{gathered} h^2=((5)/(13))^2+y^2 \\ h=\sqrt[]{(25)/(169)+y^2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/8o3pj61sxzd3ql6pgr533lunfitwkj2ofw.png)
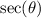
is equal to hypotenuse by adjacent.
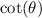
is equal to adjacent by opposite.
In the fourth quadrant,
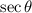
is positive , and
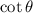
is negative.
So,
![\begin{gathered} \sec \theta=(h)/((5)/(13)) \\ =\frac{13\sqrt[]{(25)/(169)+y^2}}{5} \\ \cot \theta=((5)/(13))/(-y) \\ =-(5)/(13y) \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/okknp53x2ee4sbo7t2ibpbdf8xumg9dgaa.png)