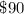Answer:
The amount of interest she will be paid in the first 3 years is;
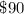
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that Lashonda deposits $500 into an account that pays simple interest at a rate of 6% per year. for the first 3 years;
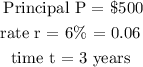
Recall the simple interest formula;
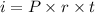
substituting the given values;
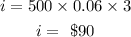
Therefore, the amount of interest she will be paid in the first 3 years is;