Given that the mean and standard deviation of the population are $24,215 and $3712 respectively,
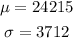
The sample size taken is 80,

Consider that the salary of students in the sample is assumed to follow Normal Distribution with mean and standard deviation as follows,
![\begin{gathered} \mu_x=\mu\Rightarrow\mu_x=24215 \\ \sigma_x=\frac{\sigma}{\sqrt[]{n}}=\frac{3712}{\sqrt[]{80}}\approx415 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/po2b7w5kh5au4pf0ssm02pja0pfxohsemo.png)
So the probability that the mean salary (X) is $24250 or more, is calculated as,
![\begin{gathered} P(X\ge24250)=P(z\ge(24250-24215)/(415)) \\ P(X\ge24250)=P(z\ge0.084) \\ P(X\ge24250)=P(z\ge0)-P(0From the Standard Normal Distribution Table,[tex]\begin{gathered} \emptyset(0.08)=0.0319 \\ \emptyset(0.09)=0.0359 \end{gathered}]()
So the approximate value for z=0.084 is,
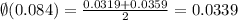
Substitute the value in the expression,
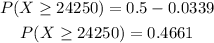
Thus, there is a 0.4661 probability that the mean salary offer for these 80 students is $24,250 or more.