Given,
The length of the rods;
L=0.780 m
l=0.500 m
The angular acceleration, α=0.750 rad/s²
The masses;
m_A=4.00 kg
m_B=3.00 kg
m_C=5.00 kg
m_D=2.00 kg
The moment of inertia of the given system of masses is given by,
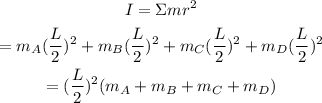
Where r is the distance between each mass and the axis of rotation.
On substituting the known values,

The torque required is given by,
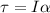
On substituting the known values,
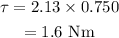
Thus the torque that must be applied to cause the required acceleration is 1.6 Nm