A) To find the length AC, we must use the trigonometric ratio
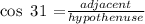
adjacent = 5cm
hypothenuse = AC
![\begin{gathered} \cos 31\text{ = }(5)/(AC) \\ AC\text{ = }(5)/(\cos 31) \\ AC\text{ =}5.8332\operatorname{cm} \end{gathered}]()
B) To find the length AB, we will use the value of AC just obtained to get it
since triangle ABC is a right-angled triangle, we will use Pythagoras theorem
so that
|AC|^2 = |AB|^2 +|BC|^2
AC = 5.8332cm
BC = 4cm
|AB|^2 = |AC|^2 - |BC|^2
![\begin{gathered} AB\text{ = }\sqrt[]{5.8332^2-4^2} \\ AB\text{ = }\sqrt[]{18.0262224} \\ AB\text{ = 4.245729883cm} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/bj3n6f1bhzy8kq16qf7ik8l1gusuex43kj.png)
C) The perimeter of the quadrilateral can be found by adding the length of all the sides around its edges.
Perimeter = AD +CD + BC + AB
We do not have CD and we must find CD
![\begin{gathered} CD\text{ = }\sqrt[]^2 \\ CD\text{ =}\sqrt[]{5.8332^2-5^2} \\ CD\text{ =}\sqrt[]{9.02622224} \\ CD\text{ = 3.004366195cm} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/high-school/yl6rnphs8rgzlhgsn4q8x1qvn5xaqlv3ay.png)
Perimeter of ABCD = 5 + 3.004366195 + 4 +4.245729883 = 16.25009708cm
D) To find the area of the quadrilateral we must find the area of triangle ADC and triangle ABC.
Area of triangle ADC = 1/2 x base x height= 1/2 x 3.004366195 x 5 = 7.510915488 square centimeter
Area of triangle ABC = 1/2 X base x height = 1/2 x 4 x 4.245729883 =8.491459766 square centimeter
Area of quadrilateral ABCD = 7.510915488 + 8.491459766 = 16.00237525 square centimeter