We will substitute the variable x with the variable u using the following relation:
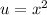
Then, we can convert the polynomial as:
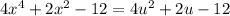
We can use the quadratic equation to calculate the roots of u:
![\begin{gathered} u=\frac{-2\pm\sqrt[]{2^2-4\cdot4\cdot(-12)}}{2\cdot4} \\ u=\frac{-2\pm\sqrt[]{4+192}}{8} \\ u=\frac{-2\pm\sqrt[]{196}}{8} \\ u=(-2\pm14)/(8) \\ u_1=(-2-14)/(8)=-(16)/(8)=-2 \\ u_2=(-2+14)/(8)=(12)/(8)=1.5 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/z6ldyurfdlvcjx4c8l1mkb52o5mpyxauux.png)
We have the root for u: u = -2 and u = 1.5.
As u = x², we have two roots of x for each root of u.
For u = -2, we will have two imaginary roots for x:
![\begin{gathered} u=-2 \\ x^2=-2 \\ x=\pm\sqrt[]{-2} \\ x=\pm\sqrt[]{2}\cdot\sqrt[]{-1} \\ x=\pm\sqrt[]{2}i \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/gwksa5dil41omnuiqdjkjrp9fbxzrijml0.png)
For u = 1.5, we will have two real roots:
![\begin{gathered} u=1.5 \\ x^2=1.5 \\ x=\pm\sqrt[]{1.5} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/e1mf0gvap8q9hy9180aaulfayq2vidsi21.png)
Then, for x, we have two imaginary roots: x = -√2i and x = √2i, and two real roots: x = -√1.5 and x = √1.5.
Answer:
Let u = x²
Equation using u: 4u² + 2u - 12
Solve for u: u = -2 and u = 1.5
Solve for x: x = -√2i, x = √2i, x = -√1.5 and x = √1.5
Imaginary roots: x = -√2i and x = √2i
Real roots: x = -√1.5 and x = √1.5