The given equation is
![\sqrt[3]{1+x+√(1+2x)}=2](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/g66a6itr38laovs8expufw89p0wtt1w9gl.png)
First, we need to elevate each side to the third power.
![\begin{gathered} (\sqrt[3]{1+x+√(1+2x)})^3=(2)^3 \\ 1+x+√(1+2x)=8 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/og405ivifzmglrqinl96f2j4i171rmvnor.png)
Second, subtract x and 1 on both sides.
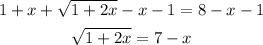
Third, we elevate the equation to the square power to eliminate the root
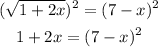
Now, we use the formula to solve the squared binomial.
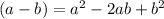
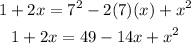
Now, we solve this quadratic equation
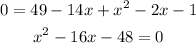
We need to find two number which product is 48 and which difference is 16. Those numbers are 12 and 4, we write them down as factors.
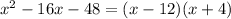
So, the possible solutions are
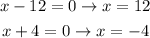
However, we need to verify each solution to ensure that each of them satisfies the given equation. We just need to evaluate it with those two solutions.
![\begin{gathered} \sqrt[3]{1+x+√(1+2x)}=2\rightarrow\sqrt[3]{1+12+√(1+2(12))}=2 \\ \sqrt[3]{13+√(1+24)}=2 \\ \sqrt[3]{13+√(25)}=2 \\ \sqrt[3]{13+5}=2 \\ \sqrt[3]{18}=2 \\ 2.62=2 \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/d5s8fisfpr35nysieoc7ggp6cu0bkkxb9h.png)
As you can observe, the solution 12 doesn't satisfy the given equation.
Therefore, the only solution is -4.