We need to first write the balanced equation:
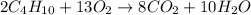
we are given the following:
mass of butane = 29.0 g
mass of carbon = 88.0 g
mass of water = 45.0 g
We want the mass of O2 that reacted.
C4H10 is the limiting reactant, and we know the masses of products produced. We can use that to find out how much oxygen reacted.
We can use CO2:
number of moles of CO2 = 88.0/44.01 = 1.9995 mol
The molar ratio between O2 and CO2 is 13:8
Therefore the number of moles of O2 = 1.9995 x (13/8) = 3.249 mol
Now that we have the number of moles, we can calculate the mass.
m = n x M
m = 3.249 mol x 31.998 g/mol
m = 103.97 g