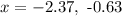The general formula for a quadratic equation is ax² + bx + c = 0.
To solve
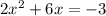
You can follow the steps.
Step 01: Write the equation in the general formula.
To do it, add 3 to each side of the equation.
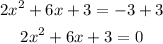
Step 02: Use the Bhaskara formula to find the roots.
The Bhaskara formula is:
![x=\frac{-b\pm\sqrt[]{\Delta}}{2\cdot a},\Delta=b^2-4\cdot a\cdot c](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/9l0o9sxw90lqvweexuahakdikegvg8acol.png)
In this question,
a = 2
b = 6
c = 2
So, substituting the values:
![\begin{gathered} \Delta=b^2-4\cdot a\cdot c \\ \Delta=6^2-4\cdot2\cdot3 \\ \Delta=36-24 \\ \Delta=12 \\ \\ x=\frac{-6\pm\sqrt[]{12}}{2\cdot2} \\ x=\frac{-6\pm\sqrt[]{2\cdot2\cdot3}}{4} \\ x=\frac{-6\pm2\cdot\sqrt[]{3}}{4} \\ x_1=\frac{-6+2\sqrt[]{3}}{4}=\frac{-3+\sqrt[]{3}}{2} \\ x_2=\frac{-6-2\sqrt[]{3}}{4}=\frac{-3-\sqrt[]{3}}{2} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/pnps7tpj1wpgkfok05wvmr1wc9mg4xdvv8.png)
Answer:
Exact form:
![x=\frac{-3-\sqrt[]{3}}{2},\frac{-3+\sqrt[]{3}}{2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/mhrlf00vawg8y0o3bxijq9954m4isdzki7.png)
Decimal form: