We have the equation:
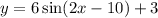
We have to find the amplitude, the period, the horizontal shift and the midline.
The amplitude can be calculated as half the difference between the maximum and minimum value of the function.
The maximum value will happen when the sine is equal to 1 and the minimum when the sine is equal to -1.
We can then calculate the amplitude A as:
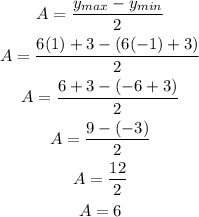
Now we have to calculate the period.
The period will be equal to the horizontal distance at which the function starts repeating itself (or complete a period).
As we have a sine function we know that:
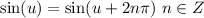
That means that it will repeat itself for any multiple of 2π.
We can calculate the period as:
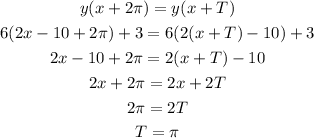
The period is π.
The horizontal shift will be given by the constant value inside the argument of the sine function. We can ignore the other terms and factors and use only the sine function in this case.
For example, for sin(2x) = 0, this value corresponds to x = 0.
In the case of sin(2x-10) = 0 this corresponds to an x that is 5.
That is because the function has a frequency that is twice as the frequency of the hpure sine function.
If the function wasn't periodice we would see it translated by 10 to the right.
We can calculate the midline as the average of the function.
This average value will be given by the average value of the sine function, which is 0, so we can calculate the midline as:
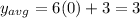
Answer:
The amplitude is 6.
The period is π.
The horizontal shift is 10 units to the right.
The midline is y = 3.