There are two forces acting on the woman: the normal force of the floor of the elevator and the weight of the woman.
First, find the weight of the woman by multiplying its mass times the acceleration of gravity:
![\begin{gathered} W=mg \\ =(57.6\operatorname{kg})(9.8(m)/(s^2))=564.48N \end{gathered}]()
According to Newton's Second Law of Motion, the net force acting on an object relates to the acceleration of the object according to:
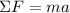
Since the normal force of the floor is exerted upwards and the weight is exerted downwards, then:
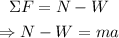
Isolate the acceleration from the equation:
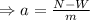
Replace the values of the normal force (395N), the weight and the mass of the woman to find the acceleration of the elevator:
![\begin{gathered} \Rightarrow a=\frac{395N-564.48N}{57.6\operatorname{kg}}=-2.94236\ldots(m)/(s^2) \\ \therefore a\approx-2.9(m)/(s^2) \end{gathered}]()
Then, the acceleration of the elevator is 2.9 m/s^2 downwards.
Use the definition of acceleration to find the final speed of the elevator 4 seconds after the initial speed of 1.50 m/s downwards:
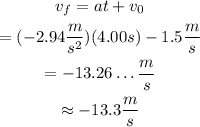
Therefore, the answers are:
The acceleration of the elevator is 2.9 m/s^2 downwards.
The final speed of the elevator 4 seconds after it had a speed of 1.50 m/s downwards, is 13.3 m/s downwards.