Use the elimination method to solve the given system of equations.
To do so, multiply the first equation by -3 so that the coefficient of x in the first equation becomes the additive inverse of the coefficient of x in the second equation:
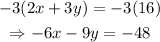
Then, the system is equivalent to:
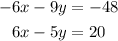
Add both equations to eliminate the variable x and to obtain an equation in terms of the variable y only:
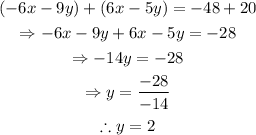
Replace y=2 into the first equation to find the value of x:
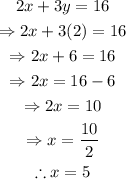
Replace y=2 and x=5 into the second equation to confirm the answer:
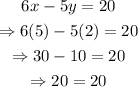
Therefore, the solution to the system of equations is x=5, y=2.