Recall the definition of the cosecant function in terms of the sine function:
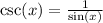
Draw the angle -210º in the unit circle to find a reference triangle for that angle:
Notice that a 30-60-90 triangle is formed:
Since the side opposite to the 30º angle has a length of 1/2, then:
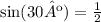
On the other hand, notice that since the angle of -210º lies in the second quadrant, then the value of sin(-210º) is positive:
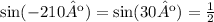
Use the definition of the cosecant function to find csc(-210º):
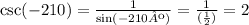
Therefore, the value of csc(-210º) is equal to 2.