Problem #2
Given the diagram of the statement, we have:
From the diagram, we see that we have two triangles:
Triangle 1 or △ADP, with:
• angle ,θ,,
,
• hypotenuse ,h = AP,,
,
• adjacent cathetus, ac = AD = x cm.
,
• opposite cathetus ,oc = DP,.
Triangle 2 or △OZP, with:
• angle θ,
,
• hypotenuse, h = OP = 4 cm,,
,
• adjacent cathetus, ac = ZP = AP/2,.
(a) △ADP: sides and area
Formula 1) From geometry, we know that for right triangles Pitagoras Theorem states:
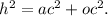
Where h is the hypotenuse, ac is the adjacent cathetus and oc is the opposite cathetus.
Formula 2) From trigonometry, we have the following trigonometric relation for right triangles:
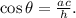
Where:
• θ is the angle,
,
• h is the hypotenuse,
,
• ac is the adjacent cathetus.
(1) Replacing the data of Triangle 1 in Formulas 1 and 2, we have:
![\begin{gathered} AP^2=AD^2+DP^2\Rightarrow DP=\sqrt[]{AP^2-AD^2}=\sqrt[]{AP^2-x^2\cdot cm^2}\text{.} \\ \cos \theta=(AD)/(AP)=(x\cdot cm)/(AP)\text{.} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/uz52zpd185b7vsrubpdztjeqai1j88ufvq.png)
(2) Replacing the data of Triangle 2 in Formula 2, we have:
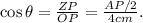
(3) Equalling the right side of the equations with cos θ in (1) and (2), we get:
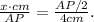
Solving for AP², we get:
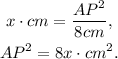
(4) Replacing the expression of AP² in the equation for DP in (1), we have the equation for side DP in terms of x:
![DP^{}=\sqrt[]{8x\cdot cm^2-x^2\cdot cm^2}=\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}\cdot cm\text{.}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/hudyyiqlcel3zuka0gqewju2uuoc0x3yzp.png)
(ii) The area of a triangle is given by:
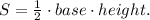
In the case of triangle △ADP, we have:
• base = DP,
,
• height = AD.
Replacing the values of DP and AD in the formula for S, we get:
![S=(1)/(2)\cdot DP\cdot AD=(1)/(2)\cdot(\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}\cdot cm)\cdot(x\cdot cm)=(x)/(2)\cdot\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}\cdot cm^2.](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/3gsfn8qp91lxy4ymux3ubqie545oivj7ds.png)
(b) Maximum value of S
We must find the maximum value of S in terms of x. To do that, we compute the first derivative of S(x):
![\begin{gathered} S^(\prime)(x)=(dS)/(dx)=(1)/(2)\cdot\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}\cdot cm^2+(x)/(2)\cdot(1)/(2)\cdot(8-2x)/(√(x\cdot(8-x)))\cdot cm^2 \\ =(1)/(2)\cdot\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}\cdot cm^2+(x)/(2)\cdot\frac{(4-x^{})}{\cdot\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}}\cdot cm^2 \\ =(1)/(2)\cdot\frac{x\cdot(8-x)+x\cdot(4-x)}{\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}}\cdot cm^2 \\ =\frac{x\cdot(6-x)}{\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}}\cdot cm^2\text{.} \end{gathered}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/srv37u8iblmaotgvef3ikhzgyvii0xex3t.png)
Now, we equal to zero the last equation and solve for x, we get:
![S^(\prime)(x)=\frac{x\cdot(6-x)}{\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}}\cdot cm^2=0\Rightarrow x=6.](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/yl1m91atti3cdnda477vz7z5qxh2fk6wla.png)
We have found that the value x = 6 maximizes the area S(x). Replacing x = 6 in S(x), we get the maximum area:
![S(6)=(6)/(2)\cdot\sqrt[]{6\cdot(8-6)}\cdot cm^2=3\cdot\sqrt[]{12}\cdot cm^2=6\cdot\sqrt[]{3}\cdot cm^2.](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/mkwrnj768avyzue2k5d8i7y5wb9szzjnkl.png)
(c) Rate of change
We know that the length AD = x cm decreases at a rate of 1/√3 cm/s, so we have:
![(d(AD))/(dt)=(d(x\cdot cm))/(dt)=(dx)/(dt)\cdot cm=-\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{3}}\cdot(cm)/(s)\Rightarrow(dx)/(dt)=-\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{3}}\cdot(1)/(s)\text{.}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/qraw10vmnnj77b43g6mxjirfxsurv9e39s.png)
The rate of change of the area S(x) is given by:
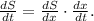
Where we have applied the chain rule for differentiation.
Replacing the expression obtained in (b) for dS/dx and the result obtained for dx/dt, we get:
![(dS)/(dt)(x)=(\frac{x\cdot(6-x)}{\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}}\cdot cm^2\text{)}\cdot(-\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{3}}\cdot(1)/(s)\text{)}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/u6fo56klthzkd07w5hr65p9zsbihvwwm2h.png)
Finally, we evaluate the last expression for x = 2, we get:
![(dS)/(dt)(2)=(\frac{2\cdot(6-2)}{\sqrt[]{2\cdot(8-2)}}\cdot cm^2\text{)}\cdot(-\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{3}}\cdot(1)/(s))=-\frac{8}{\sqrt[]{12}}\cdot\frac{1}{\sqrt[]{3}}\cdot(cm^2)/(s)=-\frac{8}{\sqrt[]{36}}\cdot(cm^2)/(s)=-(8)/(6)\cdot(cm^2)/(s)=-(4)/(3)\cdot(cm^2)/(s).](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/nth2cz31dshizmglbl9hwxgzc1qdq5z035.png)
So the rate of change of the area of △ADP is -4/3 cm²/s.
Answers
(a)
• (i), Side DP in terms of x:
![DP(x)=\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}\cdot cm\text{.}](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/hkpsj0t6ty35wz5diuvho807qo2sj39z3x.png)
• (ii), Area of ADP in terms of x:
![S(x)=(x)/(2)\cdot\sqrt[]{x\cdot(8-x)}\cdot cm^2.](https://img.qammunity.org/2023/formulas/mathematics/college/nafm2ge1pyepcnfd2fhl792doj0wbpomhd.png)
(b) The maximum value of S is 6√3 cm².
(c) The rate of change of the area of △ADP is -4/3 cm²/s when x = 2.